What is Suricata in Cyber Security?
Suricata is a powerful and versatile open-source cybersecurity tool that functions as both an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) with additional Network Security Monitoring (NSM) capabilities. It is widely used by organizations of all sizes to protect their networks by detecting and preventing cyber threats. Suricata's strength lies in its ability to handle large volumes of network traffic data while offering deep analysis capabilities and extensive customization options.
In this introductory guide to Suricata, we will explore:
- Suricata’s Functionalities
- Benefits and Disadvantages
- Basic Installation Process
- Options for Suricata GUI
What is Suricata in Cyber Security?
Suricata is a free, open-source IDS/IPS cybersecurity tool that acts as both an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS). It is used by organizations all around the world to detect cyber threats and monitor networks for suspicious activity.
Suricata’s strength lies in its versatility. When tuned correctly, it is a high-performance tool that can handle large volumes of network traffic and generate vast amounts of network traffic data. It is also extremely flexible, offering deep analysis of various protocols and the ability to customize rule sets to fit your organization’s specific needs. Because it’s an open-source IDS/IPS, Suricata benefits from a large, active community that constantly develops and refines its capabilities.
Put simply, Suricata is a powerful and adaptable tool that provides a robust layer of defense for any organization’s network security strategy.
Is Suricata an IDS or IPS?
Suricata is both an intrusion detection system (IDS) and an intrusion prevention system (IPS), but many people are unaware that it also functions as a network security monitoring (NSM) tool.
In its IDS mode, Suricata continuously monitors your network traffic for suspicious activity. It compares this traffic to a vast database of known threats and pre-defined rules. Users can also include new rule sets and create custom rules. If it detects a potential attack, like malware or a hacking attempt, Suricata issues an alert, allowing you to investigate and take action.
IDS monitoring is more passive than IPS. Suricata monitors the network traffic but does not intervene. This offers a valuable first line of defense, but some organizations might feel overwhelmed by the number of alerts and the presence of false positives, requiring human intervention to sort through alerts to find actual serious and imminent threats.
You can also configure Suricata as IPS. In IPS mode, it doesn't just detect threats, but it actively blocks them. By analyzing traffic patterns and comparing them to its rule set, Suricata can identify and stop malicious attempts before they infiltrate your system. This is a more active strategy than IDS, but false positives could lead to legitimate traffic being blocked due to poorly configured rules. Configuring Suricata as IPS while avoiding unintended consequences requires a deep understanding and expertise in network security.
Choosing between Suricata’s IDS and IPS modes depends on your organization’s unique needs. IDS is a good starting point for monitoring and gaining visibility into network threats. But if you need a more immediate response and can tolerate the risk of false positives, IPS could be a valuable addition to your security arsenal.
Is Suricata Open-Source?
Suricata is an open-source cybersecurity tool. Its code is freely available and licensed under the General Public License (GPL) version 2.0. There are several key benefits to using open-source intrusion detection tools like Suricata:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Open-source means free. You don't have to pay licensing fees for Suricata itself, making it an attractive option for organizations with limited security budgets.
- Transparency and Trust: The open-source nature allows anyone to examine Suricata's code. This transparency builds trust in the tool's functionality and helps identify any potential vulnerabilities.
- Active Community and Development: Open-source tools like Suricata benefit from a large and active community of developers. This community contributes to ongoing development, adding new features, fixing bugs, and keeping the tool up-to-date with the latest threats.
- Customization: Because the code is open, users can modify Suricata to fit their specific needs so long as they stay compliant with the GPL2. This can help tailor rule sets to address unique vulnerabilities within your network or integrate Suricata with other security tools you use.
- Flexibility: Open-source tools often offer greater flexibility in deployment options. You can install Suricata on a variety of platforms and tailor its configuration to your specific network environment.
- Shared Knowledge: The open-source community fosters knowledge sharing. Users can learn from each other's experiences, troubleshoot issues collaboratively, and contribute to the overall improvement of the tool.
However, it's important to consider some potential drawbacks to open-source intrusion detection tools as well. Open-source tools might require more technical expertise to set up and maintain compared to some commercial offerings. Additionally, while the community provides valuable support, it might not be the same level of dedicated support offered by some commercial vendors.
Is Suricata Free?
Because of its open-source nature, Suricata is free to use in line with the GPL2. It is important to note that despite being free, other costs could result from a Suricata installation:
- Hardware: Suricata can be resource-intensive, especially when dealing with high volumes of network traffic. You might need to invest in additional hardware with sufficient processing power and memory to run Suricata effectively. This could involve upgrading or purchasing new servers or other infrastructure.
- Setup and Configuration: While Suricata offers a user-friendly interface, proper configuration requires a good understanding of network security concepts and IDS/IPS functionalities. If your IT team lacks this expertise, you might need to hire consultants to help with the initial setup and configuration.
- Maintenance and Updates: Open-source thrives on community contributions, but keeping Suricata up-to-date with the latest rule sets and bug fixes might require some effort from your security team. If you don't have the internal resources, you might consider paid subscription services that offer automated updates and rule management for Suricata.
- Training: Using Suricata effectively often requires training for your IT security personnel. They'll need to understand how to interpret Suricata's alerts, investigate potential threats, and fine-tune the rule sets for optimal performance. Training can be done internally or through external providers.
- Integration with other security tools: Suricata can be a powerful tool, but it might not be the only one in your security arsenal. Integrating Suricata with other security tools like firewalls, SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems, and threat intelligence feeds can enhance its effectiveness. Depending on the chosen tools, there might be additional licensing or integration costs involved.
Overall, while Suricata itself is free, there can be some indirect costs associated with its implementation and ongoing use. The extent of these costs will depend on your specific needs, existing infrastructure, and internal IT expertise.
Is Suricata a SIEM?
No, Suricata is not a SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) system. They serve different purposes within cybersecurity, though they can work together effectively. Suricata is an IDS/IPS, primarily focusing on analyzing network traffic data packets with predefined rules and signatures to identify and potentially block malicious activity. A SIEM system is a much broader security tool. It acts as a central hub that collects, aggregates, analyzes, and stores security event data from various sources, which could include Suricata, firewalls, servers, applications, and more. SIEMs essentially offer a wider lens, helping your organization correlate security events across the entire IT environment.
Suricata and SIEM can be a powerful combination. Suricata provides real-time network traffic analysis, while SIEM collects and analyzes data from Suricata alongside other security tools. This comprehensive view allows for better threat detection, investigation, and incident response.
What is the Purpose of Suricata?
The overall purpose of Suricata is to provide network security support by identifying or blocking malicious traffic entering the network. Whether it is used in IDS or IPS mode, Suricata’s purpose is to provide a layer of defense using:
- Threat Detection: Suricata constantly examines network traffic for malicious patterns. It compares this traffic to a vast database of known attack signatures and pre-defined Suricata rules. These signatures are like the fingerprints of specific threats, allowing Suricata to identify malware, exploit attempts, and suspicious network activity.
- Deep Packet Inspection: Suricata inspects data packets, analyzing not just the source and destination, but also the content itself. This allows it to detect hidden threats within encrypted traffic or files being transferred.
- Protocol Analysis: Suricata can analyze a wide range of network protocols, understanding how different types of communication work. This lets it identify suspicious behavior within specific protocols, like unusual data transfers or attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in certain communication methods.
- Network Traffic Baselining: Suricata can be used to establish a baseline of what "normal" traffic looks like on your network. By monitoring activity over time, a machine learning engine can use the data produced by Suricata to learn the typical patterns and identify significant deviations that might indicate a potential attack.
- Threat Hunting: Suricata's detailed logs and analysis capabilities are valuable for security professionals. They can use Suricata's data to investigate suspicious activity, identify trends, and proactively hunt for hidden threats within the network.
What are the Benefits of Suricata?
Suricata offers a compelling set of benefits that make it a valuable tool for fortifying your network security. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Speed: Unlike some other IDS tools, Suricata is natively multi-threaded, meaning it can use multiple CPU cores simultaneously. This allows it to handle complex tasks and analyze vast amounts of traffic in real time, ensuring threats are detected quickly without compromising network performance. Suricata is also designed to manage memory efficiently, minimizing resource consumption and maximizing processing speed.
- Scalability: Suricata can easily adapt to your organization’s needs as it grows. It can be deployed in a distributed fashion, with sensors strategically placed across your network. This allows for wider network coverage and the ability to scale processing power by adding more sensors as your network expands. It can then be configured to prioritize specific network segments or workloads, ensuring optimal performance for critical areas while efficiently handling less sensitive traffic. Because Suricata is so efficient, it can run effectively even on modest hardware, such as the Raspberry Pi Mini Computer. As your organization’s needs grow, you can upgrade hardware or leverage distributed deployments for continued scalability.
- Flexibility: Suricata offers a high degree of customization through extensive rule sets and indicators of compromise (IOCs). Suricata supports various rule sets from multiple sources, including Emerging Threats and Snort rules. You can also create custom rules to address specific vulnerabilities or concerns. Additionally, Suricata can be configured to detect specific indicators associated with known threats, such as malicious IP addresses, URLs, or file hashes. This allows for highly targeted threat detection.
- NSM Functionality: Suricata goes beyond basic IDS/IPS functionalities, tracking network flows to provide valuable insights into network activity patterns and identifying suspicious connections. Suricata can collect various network telemetry data, including packet size, source and destination information, protocol details, and more. This comprehensive data aids in network behavior analysis and threat detection.
- Depth of Data: Suricata provides a wealth of valuable data for various security purposes, including detailed packet inspection, flow data, alert logs, and more. This data is invaluable for forensic analysis after a security breach and can be used for security audits and compliance purposes. Additionally, the detailed data Suricata provides can be fed into your organization’s SIEM, other dedicated security analytics platforms, or a network detection and response (NDR) system to be leveraged by machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) engines for advanced threat detection and automated incident response.
What are the Disadvantages of Suricata?
Unfortunately, no security system is perfect. Like any security tool, Suricata does have some distinct disadvantages:
- Complexity: Suricata offers a high degree of flexibility, but this can also translate to complexity. Setting up, configuring, and maintaining Suricata effectively requires a good understanding of network security concepts, IDS/IPS functionalities, and potentially scripting languages for rule customization. This can be a challenge for organizations with limited security expertise.
- False Positives: Suricata relies on predefined rules and signatures to identify threats. Overly strict or outdated rules can lead to false positives, where legitimate traffic gets flagged as suspicious. This can create unnecessary alerts and waste valuable security personnel time investigating non-existent threats.
- Performance Overhead: While Suricata is known for its speed, it can still consume significant CPU and memory resources, especially when dealing with very high-bandwidth networks. This might necessitate upgrading hardware or implementing distributed deployments to ensure optimal performance.
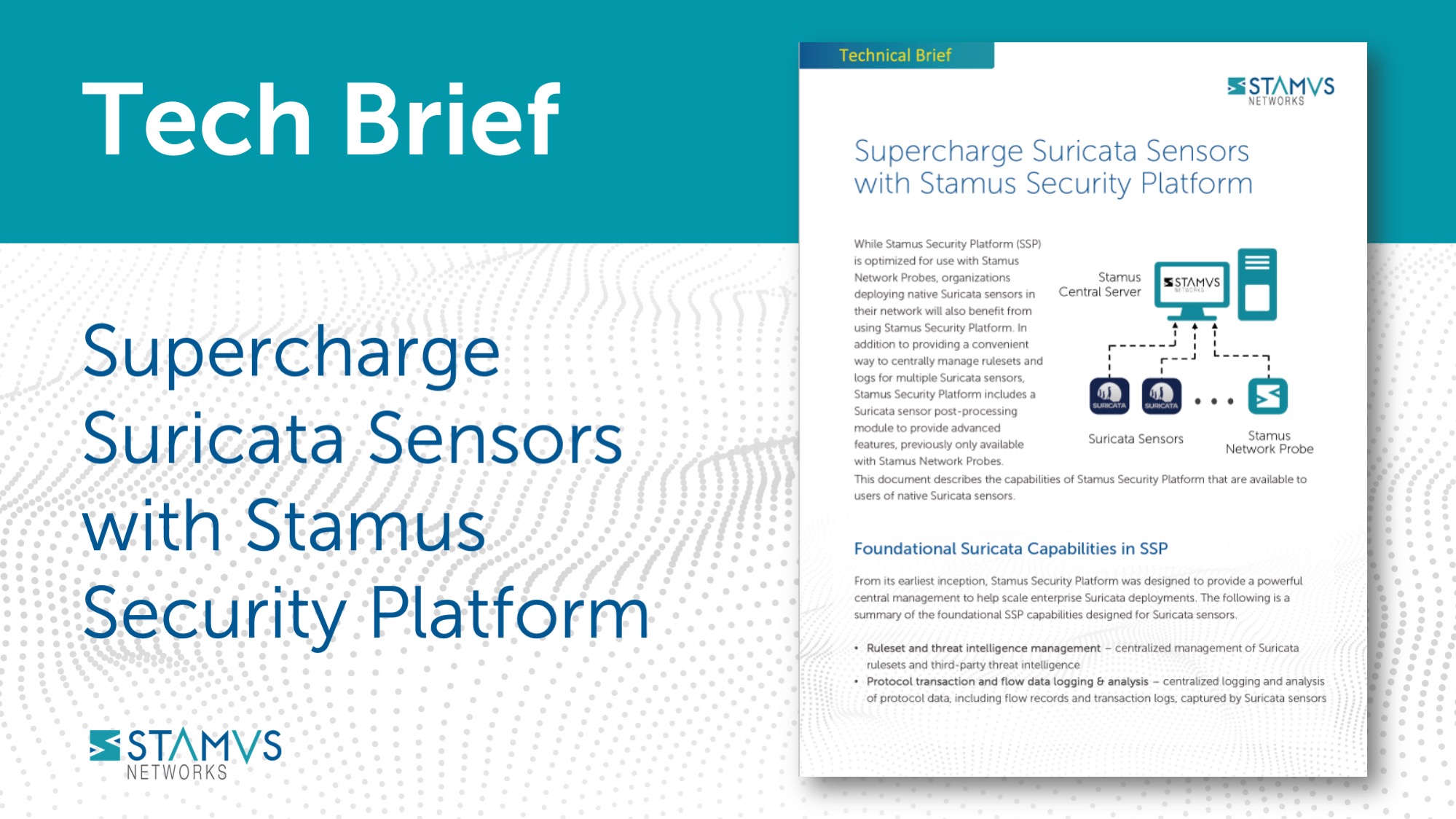
- Limited Support: Suricata being open-source offers cost advantages, but it also means there's no guaranteed vendor support. While the community is active and helpful, organizations might require additional resources or expertise to troubleshoot complex issues or integrate Suricata with other security tools. A solution to this could be implementing a Suricata-based network detection and response (NDR) system like the Stamus Security Platform.
- Security Expertise Needed: Extracting the most value from Suricata requires skilled security professionals. You'll need personnel who understand threat detection, rule management, and interpreting the vast amount of data Suricata collects. This can be a challenge for organizations with limited security staff.
- Alert Fatigue: Suricata can generate a significant number of alerts, especially in complex network environments. Without proper filtering and prioritization, security personnel can become overwhelmed by alert fatigue, potentially missing critical threats amidst the noise.
Suricata is a powerful and versatile tool, but it's not a one-size-fits-all solution. Consider the complexity, potential for resource consumption, and the need for security expertise when evaluating Suricata for your specific needs. If your organization wants to begin using Suricata, you could also consider deploying a network detection and response (NDR) system built on top of the Suricata engine, such as the Stamus Security Platform.
How to use Suricata?
Using Suricata involves several key steps:
- Installation:
- First, choose a platform. Suricata is available for various operating systems like Linux, FreeBSD, UNIX, Mac OS X, and Windows. Download the installer suitable for your chosen platform from https://suricata.io/download/. The installation process generally involves following the instructions provided by the download source using your system’s package manager, or you can compile the code if you prefer a more customized approach.
- Configuration:
- Suricata relies on a configuration file to define its operational parameters. The file specifies details like network interfaces to monitor, rule sets to use, logging options, and potential actions for detected threats. Popular options for rule sets include those available from Emerging Threats (ET) and Snort rules. You can also create custom rules to address specific vulnerabilities or concerns within your network.
- Running Suricata:
- Once configured, you can initiate Suricata using the appropriate system commands (e.g., systemctl start suricata on some Linux distributions).
- Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Regularly review Suricata logs to identify potential threats and investigate suspicious activity. Make sure to also keep Suricata's rule sets updated with the latest threat signatures to ensure optimal protection. This may involve periodic manual updates or setting up automated update mechanisms. Always make sure to monitor Suricata's resource consumption (CPU, memory) to ensure it's functioning optimally. You might need to adjust configurations or upgrade hardware if performance bottlenecks occur.
- Additional Tips:
- Start with a Basic Setup: Begin with a basic configuration and gradually add complexity as you gain experience with Suricata.
- Test Your Configuration: Before deploying Suricata in a production environment, thoroughly test your configuration with simulated traffic to identify and address any potential issues.
- Community Resources: The Suricata community offers a wealth of resources, including documentation, tutorials, and forums. Leverage these resources for learning and troubleshooting.
- Consider Training: If your IT team lacks experience with Suricata or IDS/IPS concepts, consider professional training to ensure effective implementation and management.
- Attend SuriCon: Every year the OISF hosts SuriCon, the world’s only major conference dedicated to Suricata development, training, and discussion.
Does Suricata Have a Web Interface?
No, Suricata itself does not have a built-in web interface. It's primarily a command-line tool with configuration files for customization. However, those desiring a web-based management experience to see Suricata dashboards should consider downloading SELKS by Stamus Networks.
SELKS is a turn-key Suricata-based IDS/NSM and threat-hunting system. It is available as either a live and installable Debian-based ISO or via Docker compose on any Linux operating system.
SELKS is comprised of the following major components:
- Suricata - Ready to use Suricata
- Elasticsearch - Search engine
- Logstash - Log injection
- Kibana - Custom dashboards and event exploration
- Stamus Community Edition (CE) - Suricata ruleset management and Suricata threat hunting interface
In addition, SELKS also includes Arkime, EveBox, and CyberChef.
SELKS is an incredibly powerful and effective way to begin learning Suricata, and for many small-to-medium sized organizations, hobbyists, and educational settings SELKS functions as a production-grade NSM and IDS solution.
To download SELKS or learn more, please visit www.stamus-networks.com/selks.
Learn More About Suricata
Suricata provides a solid first layer of defense for any organization's network security strategy. Its open-source nature offers cost-effectiveness, transparency, and a thriving community for ongoing development and support. While some technical expertise is required for setup and maintenance, Suricata's scalability, flexibility, and wealth of data it generates make it a valuable tool for organizations seeking to actively monitor and protect their networks.
To begin learning more about Suricata, we recommend downloading the open-source book published by Stamus Networks titled “The Security Analyst’s Guide to Suricata” — the first practical guide to threat detection and hunting using Suricata, the world’s most popular open-source network security engine.
Written for security operations center (SOC) analysts and threat hunters who use Suricata to gain insights into what is taking place on their networks, the book provides vital information on entry points and an in-depth analysis of the most important Suricata features.